The GainSeeker Variation Wizard helps you find the sources of variation in SPC data so you can work to improve your processes. The Variation Wizard is accessible from SPC Control charts*.
*GainSeeker Charts module control chart types from which you can open the Variation Wizard include: Control, Combination, X-Bar/Moving range/Range, Scatter, and Cusum/Control charts.
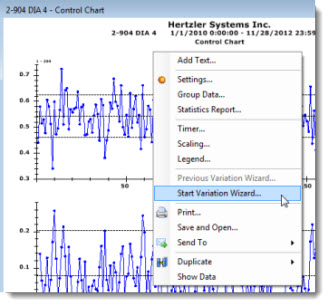
There are three ways to open the Variation Wizard from a control chart.
Right-click the chart. Then, click Start Variation Wizard... on the right-click menu that displays.
Click Options on the GainSeeker Charts window menu, and then click Start Variation Wizard... on the list that displays.
Click the Wizard button on the GainSeeker Charts toolbar.

The Variation Wizard opens.
 Tip:
You can press the F1 key any time
you are using the Variation Wizard
to open this help topic for quick reference.
Tip:
You can press the F1 key any time
you are using the Variation Wizard
to open this help topic for quick reference.
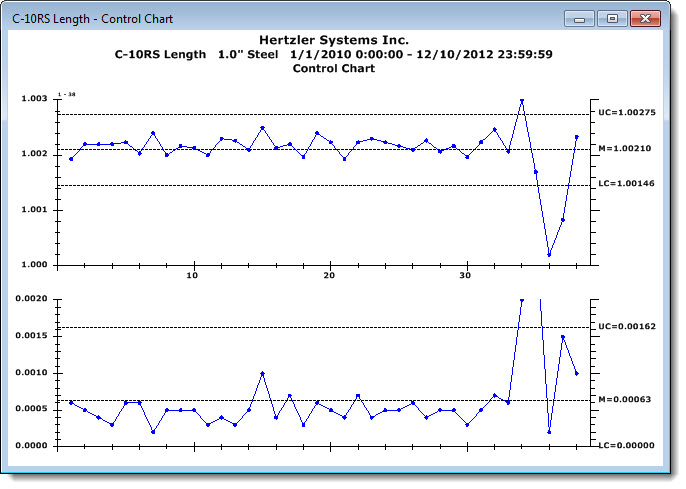
The Control chart in this example exhibits out of control points. Data points that originate from special causes should be excluded from the analysis before proceeding with the wizard analysis.
If you are unfamiliar with the system that is producing this data, you may want to study the Control chart from which you launched the Variation Wizard. You may also want to become familiar with the traceability relationships for this system so that you can make informed decisions from the Variation Wizard results.
You can also check for points out of control in the data on Step 1 of the wizard, by checking the message area diagrammed below and you can click the Stability Info button to display information about the current chart.
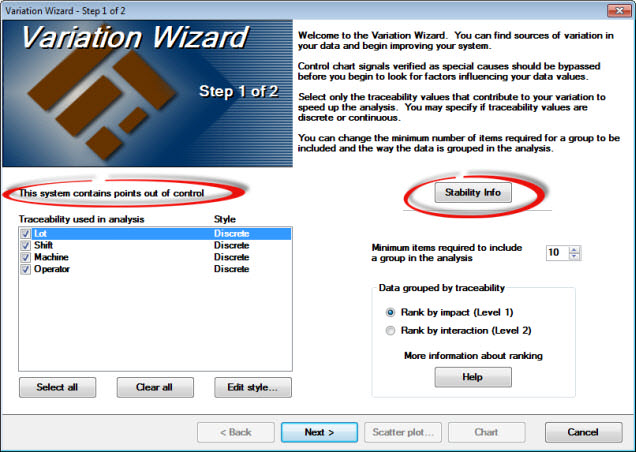
Information about the current chart used in this example displays when the Stability Info is clicked:
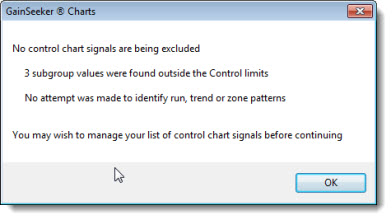
See Excluding out of control data points from the analysis below in this topic.
This example shows how it will display after all points are excluded:
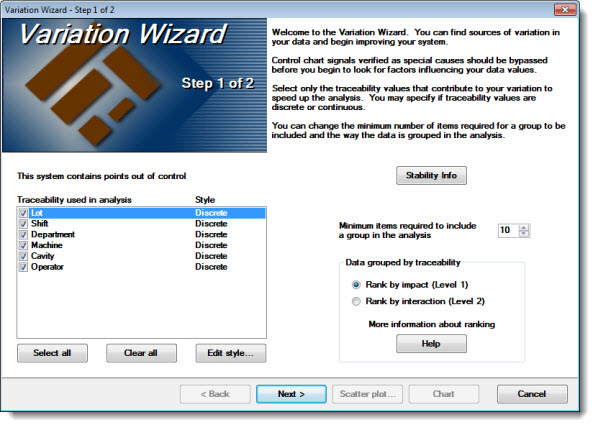
On the Variation Wizard dialog box, select only the traceability values in the Traceability used in analysis list that may be causing the most variation. This will help to hasten the analysis. Click a traceability item to select it or to clear it from the analysis. Only selected checkboxes will be used for the analysis.
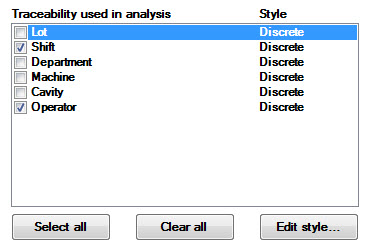
If needed, designate the style of each selected traceability as Discrete or Continuous. See Differentiating between Discrete and continuous traceability values for more information.
To change the style, click a traceability to highlight and select the row. Then, click Edit style... .
Click Discrete or Continuous on the dialog box that opens.

For more information about these options, see "How data is ranked for a Variation Wizard analysis." When you are using the wizard, you can click the Help button under More information about ranking to go directly to that topic.
Also see Level 2 analysis example
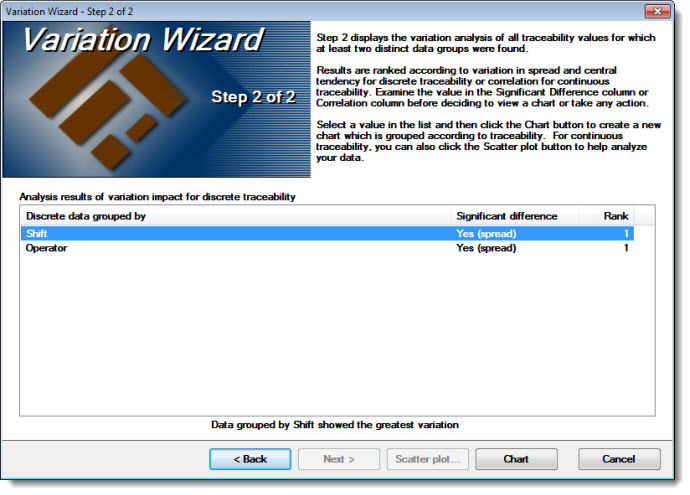
This step displays the variation analysis of all the traceability values you selected in Step 1 for which at least two distinct data groups were found. In this example, data grouped by Operator and data grouped by Shift (both ranked 1) share the most Significant difference in variation in spread for the discrete traceability.
You can draw a new chart to display the variation between groups. The results in the column labeled Rank list from top to bottom in order of variation in spread and a central tendency for discrete traceability or correlation for continuous traceability.
Next, select one or more values in the list and then click the Chart button to create new charts that are grouped according to traceability. For continuous traceability, you can click the Scatter plot button to help analyze your data.
When Shift is selected for further analysis by clicking the Chart button on the wizard, the following chart generates.

See Traceability labels and lists
If you have discrete traceability, you will have a list like the one on top where the traceability is ranked and the significance of variation between groups is based on the F-Test and t-Test results. The F-Test checks to see if the spread of two groups are significantly different, and the t-Test checks if the means of two groups are significantly different. You should start with the highest-ranked item in the list and look at the chart by the selected traceability. You may quickly decide that although the variation is significant, the differences between groups are not large enough to make any changes.