Action Taken
Corrective action performed in response to a real-time failure or other problem in the process.
AIAG
Automotive Industry Action Group.
Archive
To offload data and notes from your working database to an archive file. If you need to access the data later, you can import it from the archive file.
Cause
The root cause of a real-time failure.
Cell reference
A special formula that returns the value of the specified cell in a template. The formula is the address of the cell (column letter followed by row number) enclosed in brackets.
Example:
The formula [C1] returns the value contained in cell C1 of the template.
This file contains configuration settings specific to one workstation and exists in the Windows folder on that workstation. You can carefully modify this file to change some of the functions of the program to better meet your needs.
Data entry constant
The first part of a data value that is used consistently for one standard.
DBA
Database Administrator.
The administrator determines the content, internal structure, and access strategy for a database, defines security and integrity, and monitors performance. Specific education and certification are usually requirements for this title and its responsibilities.
DMS
Defect Management System. The GainSeeker features that deal with attribute SPC.
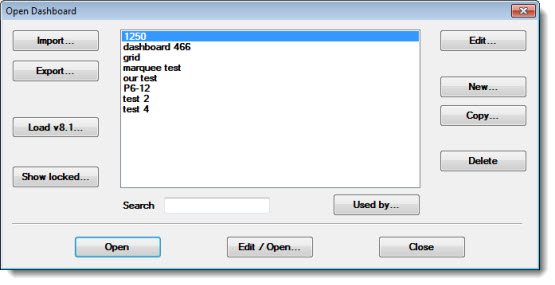
The term "dialog" is used throughout this GainSeeker Suite Online User Guide. For example, when you opt to change a setting, a dialog (sometimes also called a "dialog box") may open prompting you for information or the selection of commands. Following is an image of a sample dialog, in this example, the Open Dashboard dialog:

Editor
The default editor program is WordPad. It is possible to change this setting and to set up a second editor program with Cms.ini settings.
Here is an example of Cms.ini settings that define Microsoft Word and Microsoft Excel as the two editor programs:
editor=C:\Program Files\Microsoft Office\Office11\winword.exe
editor2=C:\Program Files\Microsoft Office\Office11\excel.exe
GainSeeker prints tables and lists to the editor program as tab-delimited text files. You cannot print a table or list directly from GainSeeker to the printer—it must be printed from the editor program. You can use the editor to add notes or formatting to the table or list before printing.
You can also choose to send charts to the editor program. When sending a chart to editor, the chart image will be followed by the default statistics to print after charts.
For more information, see the Cms.ini settings editor= and editor2=.
Event
An occurrence in your process that could be responsible for a real-time failure.
Exponential notation
A numeric format used to represent very large and very small numbers. Numbers expressed in exponential notation are displayed in two parts, a mantissa and an exponent. The mantissa specifies the digits in the number, and the exponent specifies the magnitude of the number (the position of the decimal point). For example, the numbers 314,600,000 and 0.0000451 are expressed respectively as 3146E5 and 451E-7 in exponential notation.
Gate limit
Gate limits are historical control limits that you store in the standard.
Individuals
Data with a subgroup size of one.
ODBC
Open Database Connectivity.
This programming interface provides a common language for Windows applications to access a database on a network.
Part Number
For information on differences between part numbers and standards, refer to the entry for Standard below in this topic.
Peer-to-peer network
A network without a file server. Files are shared by storing them on the hard disks of individual workstations on the network, instead of storing the files at the server.
Priority list
A "short list" of standards that is set up for one user or group name. Using priority lists saves users from scrolling through many standards they may never use by displaying a much smaller list of the standards that they use frequently.
For more information on creating priority lists, see Priority Lists.
Reasonable limits
Limits you set in the standard to catch obvious errors in data entry. When a data point falls outside the reasonable limits, the program prompts the operator to re-enter the value, because it cannot be a valid measurement for this standard. You should set reasonable limits so that the highest and lowest valid measurements for this standard fall on or just within the reasonable limits.
Registry
A central hierarchical database in Windows 95 and later that is used to store information necessary to configure the system for one or more users, applications, and hardware devices. The Registry contains information that Windows needs to continually reference during operation, such as profiles for each user, the applications installed on the computer and the types of documents each can create, property sheet settings for folders and application icons, what hardware exists on the system, and which ports are being used.
Retrieved data
In the SPC Data Entry module, this term refers to the data points used to calculate control limits during the data entry session.
Retrieved data includes the data points displayed on the real-time control chart or on the Data Table tab (if available). Depending on how your system has been configured, older data points may also be included in the retrieval for control limit calculations.
Points in a row on one side of the average. The number of points that constitutes a run may be 6, 7 or 8, depending how you configure the program. See Real-time checks for more information on configuring the number of points in a run.
RunOnce
A special subkey in the Registry.
The next time your computer is booted, any application listed in the SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\RunOnce subkey will automatically be run one time, immediately after Windows is loaded.
Serial number
A unique identifier for your license of GainSeeker. The serial number format is GSxx-xxx-xxxx.
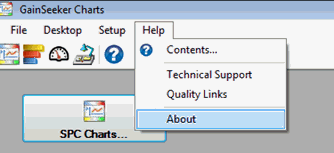
To find your serial number for GainSeeker, log in to any module of GainSeeker, click the Help menu, and then click About.
If you are unable to install the program, check the GainSeeker installation package for the serial number.
A record that defines a unique combination of part number and characteristic (SPC) or part number and process (DMS). It is the key identifier for all of the data records in the GainSeeker system. In SPC, the standard stores important data about the part number and characteristic, including specification limits. In DMS, the standard stores information such as default sample size, opportunities per unit and cost per unit.
For information on creating or editing SPC standards, see What is a standard?
For information on creating DMS standards, see DMS Standards.
Technical support
For technical assistance, contact Hertzler Systems Technical Support.
HertzlerNet members can use the email form on the Hertzler website
Email: support@hertzler.com
Phone: (574) 533-0571, ext. 2 (available 8am – 5pm EST, Monday through Friday, except on some major holidays)
Fax: (574) 533-3885
When you contact technical support by telephone, you should be at your computer and prepared to provide the serial number for your GainSeeker System. Your serial number helps the Hertzler staff to serve you more efficiently.
To find your serial number for GainSeeker, log in to any module of GainSeeker, click the Help menu, and then click About.
If you are unable to install the program, check the GainSeeker installation package for the serial number.
When you submit your question in writing, please provide as much detail about the problem and your current system as possible.
Trend
Points in a row that are consistently increasing or consistently decreasing. The number of points that constitutes a trend may be 6, 7 or 8, depending how you configure the program. See Real-time checks for more information on configuring the number of points.
A folder that contains important files for your Windows operating system.
On a Windows XP or Windows 98 workstation, the default name for this folder is Windows on the drive where Windows is installed (usually C: or D:).
On a Windows 2000 or Windows NT workstation, the default name for this folder is WinNT on the drive where Windows is installed (usually C: or D:).
On Windows Vista, each user who logs in to this workstation and runs GainSeeker will have their own settings stored in the \Users\user_name\AppData\Local\VirtualStore\Windows\ folder on the drive where Windows Vista is installed (usually C: or D:). The default settings for new GainSeeker users on this workstation are stored in the \Windows\ folder on the drive where Windows Vista is installed (usually C: or D:).
Windows\System32 folder
A folder that contains important supporting files for your Windows operating system.
On a Windows XP, Windows 2000, Windows NT, Windows 98 or Windows 95 workstation, the default name for this folder is System32 and it is located in the Windows Folder.
On Windows Vista, the default name and location of this folder is Windows\System32 on the drive where Windows is installed (usually C: or D:).
Zone
Tests for 2 out of 3 data points between 1 and 3 standard deviations from the mean, and for 4 out of 5 points outside 1 standard deviation from the mean. Data that meets either of these criteria exhibits an unusual data spread within the control limits and should be investigated for special causes of variation in the process. Even if the standard is configured such that the Lower Control limit cannot be less than zero, the zones below the mean are based on the original (non-zero) control limit value both for real-time checks and for calculating outliers.