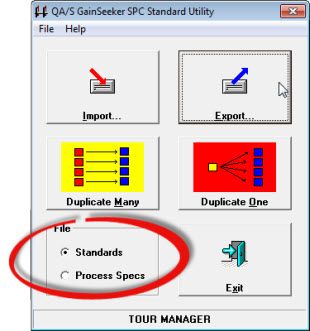
You can export and import standards and Short Run process specifications to and from text files using the SPC Standard Utility module.
Choose whether to export Standards or Process Specs. Then, click the Export.... button on the utility.

The Export Standards dialog opens.
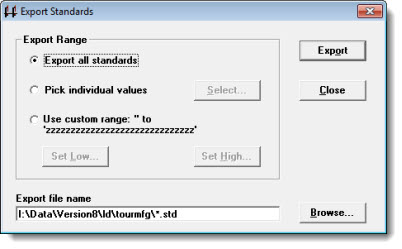
In the Export Range field of the Export Standards dialog, select the range of standards or Short Run process specifications to export:
To select all, choose Export all standards.
To select individual standards, choose Pick individual values, and then click Select. For more information, see Finding and selecting standards.
To select a range of items, choose Use custom range. Click Set Low... to set the first item in the range and then click Set High... to set the last item in the range. The low item should precede the high item in the list of standards or process specifications.
Enter a path and export file name in the Export file name box or click Browse... .
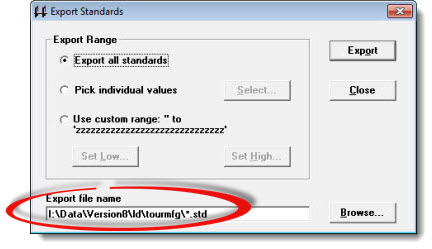
If you do not enter the export file name path in the text field, the file will be created in the SPC Standards path for the current configuration.
The file name extension that you include with the file name will determine the format of the output file. You may export to .tab (recommended), .xml, or .std (comma-separated text). If you do not specify an extension, the .std extension will automatically be used to create and format the output file.
If you click Browse, highlight an existing file to overwrite or enter a new File Name to create a new file. You can also navigate to the folder where you want to create the export file and select the type of export file to create: Tab Standards Format (*.TAB), XML Standards Format (*.XML), or Standards Format (*.STD).
After selecting the standards to export and the Export file name, click Export.
GainSeeker displays a final count of exported standards.
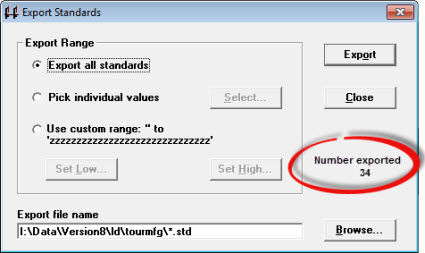
Click Close to return to the SPC Standard Utility.
Choose whether to import Standards or Process Specs. Then, click the Import... button on the utility.
The Import Standards dialog opens.
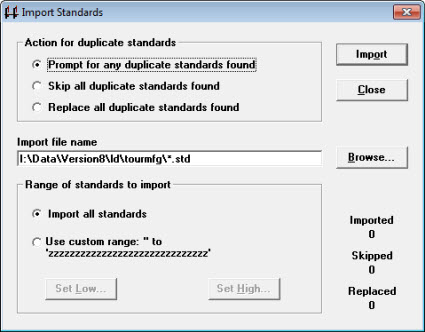
To have GainSeeker prompt you with Skip or Replace options each time a duplicate record is found during the import, choose Prompt for any duplicate standards found.
To keep the existing items in your database and skip importing any duplicate items from the text file, choose Skip all duplicate standards found.
To overwrite any existing items in your database with duplicate items from the text file, choose Replace all duplicate standards found.
Enter a name in the Import file name text box or click Browse... .
Important: The import file you select must be a text file specially formatted for importing and exporting standards: .tab, .xml or .std. You can also import .std files exported by earlier versions of SPC, which use a different format.
If you type the import file name, you can also type the path of the folder where the import file exists. If you do not type the path, the import function will look for the file name you specify in the SPC Standards path for the current configuration.
You can also click Browse... to search for the import file.
Select the Range of standards to import (or Short Run process specifications).
To select all, choose Import all standards.
To select a range of items, choose Use custom range. Click Set Low to set the first item in the range and then click Set High to set the last item in the range. The low item should precede the high item in the standards or process specifications list.

Click Import.
GainSeeker displays final counts of the standards that were imported, skipped, or replaced.
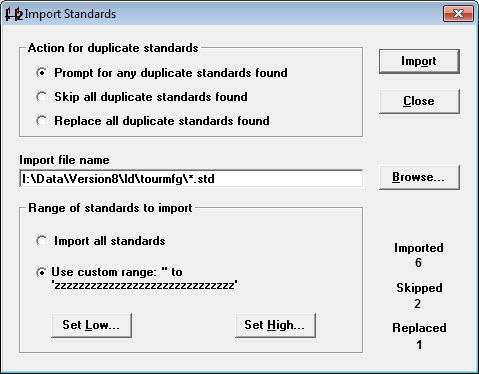
Click Close to return to the SPC Standard Utility.
The format for the *.std import file is comma-separated flat ASCII text file. You can see exactly what the file should look like by exporting data for a known standard and then examining the resulting file with a text editor such as NotePad.
The format expected by the import function follows.
Line 1: Heading information
The first line of the import file should contain all of the following values, in the order shown below, separated by commas.
The items displayed in italics depend on the labels that you have configured for these items.
Important: Values displayed below in quotation marks must be formatted with quotation marks in the import file.
|
Heading values |
Based on the user-defined label |
|
"Part Number" |
|
|
"Description" |
|
|
Subgroup size |
|
|
Range chart |
|
|
Num decimals |
|
|
Exponent |
|
|
Use exponent |
|
|
Meas system |
|
|
"Meas unit" |
|
|
"DE constant" |
|
|
Monitor |
|
|
"DMS Part Number" |
|
|
"DMS Process" |
|
|
RT checks |
|
|
Lo Spec |
|
|
Hi Spec |
|
|
Lo Gate |
|
|
Hi Gate |
|
|
Lo range Gate |
|
|
Hi range Gate |
|
|
Lo Ind. limit |
|
|
Hi Ind. limit |
|
|
Lo reas limit |
|
|
Hi reas limit |
|
|
Scale lo |
|
|
Scale hi |
|
|
Scale r |
|
|
Target x |
|
|
Target r |
|
|
"Variable 1" |
|
|
"Variable 2" |
|
|
"Variable 3" |
|
|
"Variable 4" |
|
|
Values >= 0 |
|
Example heading line
In your . std file, this heading line will look something like this:
"Part Number","Description",Subgroup size,Range chart,Num decimals,Exponent,Use exponent,Meas system,"Meas unit","DE constant",Monitor,"DMS Part Number","DMS Process",RT checks,Lo Spec,Hi Spec,Lo Gate,Hi Gate,Lo range Gate,Hi range Gate,Lo Ind. Limit,Hi Ind. Limit,Lo reas limit,Hi reas limit,Scale lo,Scale hi,Scale r,Target x,Target r,"Variable 1","Variable 2","Variable 3","Variable 4",Values >= 0
Lines 2 through the end: Standard information
Lines following the heading line should contain all of the following values, in the order shown below, separated by commas.
Important: Values displayed below in quotation marks must be formatted with quotation marks in the import file.
|
Standard fields |
Valid entries |
Example entry |
Can be blank? |
|
part number |
The name of the standard, up to 30 characters. |
"D-34KW LENGTH" |
N |
|
description |
A description of the standard, up to 14 characters. |
"blue widget" |
Y |
|
subgroup size |
Integer between 1 and 72. |
3 |
N |
|
range chart |
Range, Moving Range, or Sigma |
Range |
N |
|
number of decimals |
Integer between 0 and 10. |
3 |
N |
|
Exponent |
Non-zero integer between -323 and 307. |
0 |
Y |
|
use exponent |
True or False |
False |
N |
|
Measurement system |
English or Metric |
English |
N |
|
measurement unit |
A string of up to 10 characters. |
"Inch" |
N |
|
data entry constant |
Number up to 10 characters long. |
"0.7" |
N |
|
Monitor |
None (Never) Green (Data without failures) Red (For real-time failures) Both (For all data) |
Both |
N |
|
DMS part number |
The part number from DMS to use for defect data entry. |
"D-34KW" |
N |
|
DMS process |
The process from DMS to use for defect data entry. |
"E CUTTING" |
N |
|
real-time checks |
Integer, using the following rules: 0 No real-time checks If checking for Spec failures then add 3072. If checking for individual Gate failures then add 768. If checking for control limit failures then add 15. If checking for subgroup Gate failures then add 240. If checking for X-bar run failures then add 12288. If checking for range run failures then add 49152. If checking for X-bar trend failures then add 196608. If checking for range trend failures then add 786432. If checking for 2 of 3 zone failures then add 3145728. If checking for 4 of 5 zone failures then add 12582912. |
3087 |
N |
|
lower spec |
Lower specification limit. |
0.745 |
N |
|
upper spec |
Upper specification limit. |
0.755 |
N |
|
lower gate |
Lower gate limit. |
NONE |
N |
|
upper gate |
Upper gate limit. |
NONE |
N |
|
lower range gate |
Lower range gate limit. |
NONE |
N |
|
upper range gate |
Upper range gate limit. |
NONE |
N |
|
lower individual limit |
Lower individual limit. |
NONE |
N |
|
upper individual limit |
Upper individual limit. |
NONE |
N |
|
lower reasonable limit |
Lower reasonable limit. |
0.500 |
N |
|
upper reasonable limit |
Upper reasonable limit. |
1.000 |
N |
|
scale lower |
Lower scaling value for X-bar chart. |
NONE |
N |
|
scale upper |
Upper scaling value for X-bar chart. |
NONE |
N |
|
scale R |
Upper scaling value for R chart. |
NONE |
N |
|
target X |
Target X (nominal) value. |
0.750 |
N |
|
target R |
Target R value. |
NONE |
N |
|
variable 1 |
Standard variable 1, up to 30 characters long. |
"" |
Y |
|
variable 2 |
Standard variable 2, up to 30 characters long. |
"" |
Y |
|
variable 3 |
Standard variable 3, up to 30 characters long. |
"" |
Y |
|
variable 4 |
Standard variable 4, up to 30 characters long. |
"" |
Y |
|
Values >= 0 |
Lower Control limit cannot be less than zero |
False |
Y |
Blank values
If you are formatting a . std file for import and want to leave a field blank, you can simply avoid typing a value between the commas for that field. If the field requires quotation mark delimiters (such as the Part Number field), type just the quotation marks with no other characters between them.
For all of the limits (including specification limits, gate limits and reasonable limits), scaling values and target values, you can leave a limit blank by entering NONE or by failing to enter any characters between the commas for that field. The SPC Standard Utility will export these values as NONE if they are blank.
Length of values
If you are formatting a . std file for import, it is not necessary to pad each field with spaces so that it contains the maximum number of characters. If a value is too long or too short the SPC Standard Utility will automatically format it to the appropriate length. This also applies to users who add a space after each comma.
Case sensitivity
You can enter the values listed above in any combination of uppercase and lowercase characters, except for the values in the following fields:
Part Number
Description
Meas unit
DMS Part Number
DMS Process
These four values should be entered the way you want them to appear in GainSeeker.
Example data line
In your . std file, a data line will look something like this:
"B-34KB LENGTH A","Length",3,Range,3,0,False,English,"Inch","0.7",Red,"","",67108863,0.745,0.755,NONE,NONE,NONE,0.003,NONE,NONE,NONE,NONE,NONE,NONE,NONE,0.750,0.003,"","A","","Length",False,
Comma and period
The SPC Standard Utility uses the Windows List separator to separate values on one line of a standards export or import file. The default separator for computers using English (United States) settings is a comma.
The Standard Utility uses the Windows Decimal symbol for the decimal point. The default symbol for computers using English (United States) settings is a period.
For information on viewing or setting the Windows list separator and decimal symbol, see Regional options.