You can choose from a list of SPC statistics when performing tasks such as:
using the STAT_NUM and STAT_STR template commands to display the corresponding value or statistic in a data entry template
defining the statistics displayed on a Process Capability chart by using the multcap_1=, multcap_2=, and multcap_3= Cms.ini settings
|
Contents [Hide] |
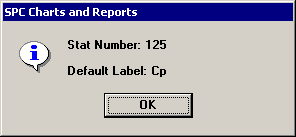
You can define
the labels used for all of these statistics. The system uses a code
number to identify each statistic when it stores items such as dashboards
and statistics list formats. You can also find these numeric codes by
generating a statistics list and then double-clicking the statistic for
which you want to find the numeric code. This will display a message similar
to the following:

Some of the default labels will automatically change if you change Shared labels such as the Part label or Process label, or if you change SPC labels such as the Individual limit label or the Spec label. These portions of the default statistics labels are displayed in italics in the tables below.
The SPC statistics can be divided into the following categories:
A few statistics appear in multiple categories.
Default label |
Explanation |
Code(s) |
Count excluded subgroups |
Number of subgroups that are excluded as outliers or bypassed records. |
8 |
Count excluded values |
Number of individual values associated with subgroups that are excluded as outliers or bypassed records. |
5 |
Number of subgroups that are not excluded as outliers or bypassed records. |
7 |
|
Count included values |
Number of individual values associated with subgroups that are not excluded as outliers or bypassed records. |
4 |
The average of all individual values for the retrieved data. |
23 |
|
Mean - nominal |
Calculated as Mean - Nominal spec |
264 |
Median |
Calculated by arranging all individual values in order and then picking the middle one. If the number of values is even, the median is the mean of the two middle numbers. The median is useful when the distribution has very large extreme values that can skew the data. |
67 |
Median range |
Calculated by arranging all range values in order and then picking the middle one. If the number of values is even, the median is the mean of the two middle numbers. |
64 and 78 |
Median subgroup |
Calculated by arranging all subgroup values in order and then picking the middle one. If the number of values is even, the median is the mean of the two middle numbers. |
61 |
Mode |
The individual data value that occurs most often. |
160 |
No data found |
Returns "Yes" if no data is found to analyze. |
285 |
The average of all range values for the retrieved data. |
24 and 25 |
|
Standard deviation of individual
values calculated by the Factors
Method: |
26 |
|
SD (range) |
Standard deviation of range values
calculated by the Sample Standard Deviation method: |
28 and 29 |
Standard deviation of individual
values calculated by the Sample
Standard Deviation method: |
27 |
|
SD (subgroup) |
Standard deviation of subgroup values
calculated by the Sample Standard Deviation method: |
286 |
Subgroup size of retrieved data. |
0 |
|
Number of subgroups in the retrieved data. This number includes excluded subgroups. |
6 |
|
Total values |
Number of individual values in the retrieved data. This number includes individual values associated with excluded subgroups. |
3 |
Default label |
Explanation |
Code |
Estimate of process capability if the process is centered between the specification limits. Process spread is based on SD (factors). |
125 |
|
Estimate of process capability if the process center moves toward one of the specification limits. Process spread is based on SD (factors). A Cpk less than zero indicates that the center of the process lies outside the specification limits. |
121 |
|
Cpm |
Estimate of process capability around a target. |
129 |
CR |
Capability ratio that is calculated as the inverse of Cp. |
123 |
PC |
The ratio of the process spread to the specification limit spread where the process spread is determined by SD (factors). |
127 |
Estimate of process performance if the process is centered between the specification limits. Process spread is based on SD (sample). |
126 |
|
PP |
The ratio of the process spread to the specification limit spread where the process spread is determined by SD (sample). |
128 |
Ppk |
Estimate of process performance if the process center moves toward one of the specification limits. Process spread is based on SD (sample). A Ppk less than zero indicates that the center of the process lies outside the specification limits. |
122 |
PR |
Performance ratio that is calculated as the inverse of Pp. |
124 |
Sigma level |
Returns the smaller of the two Z values (Zl or Zu) used to calculate process capability. |
304 |
The distance of the process average from the lower specification limits measured in standard deviation units. The standard deviation is based on factors, sample, or fit to a non-normal curve. (Zl factors, Zl SSD or Zl non-normal.) |
136 |
|
The distance of the process average from the lower specification limits measured in standard deviation units. The standard deviation is based on SD (factors). |
130 |
|
The distance of the process average from the lower specification limits measured in standard deviation units. The standard deviation is based on the non-normal curve. |
134 |
|
The distance of the process average from the lower specification limits measured in standard deviation units. The standard deviation is based on SD (sample). |
132 |
|
The distance of the process average from the upper specification limits measured in standard deviation units. The standard deviation is based on factors, sample, or fit to a non-normal curve. (Zu factors, Zu SSD or Zu non-normal.) |
137 |
|
The distance of the process average from the upper specification limits measured in standard deviation units. The standard deviation is based on SD (factors). |
131 |
|
The distance of the process average from the upper specification limits measured in standard deviation units. The standard deviation is based on the non-normal curve. |
135 |
|
The distance of the process average from the upper specification limits measured in standard deviation units. The standard deviation is based on SD (sample). |
133 |
Default label |
Explanation |
Code(s) |
EWMA LCLx |
Lower control
limit for EWMA chart: |
177 and 179 |
EWMA UCLx |
Upper control
limit for EWMA chart: |
176 and 178 |
Lower control limit for the range chart. This value is affected by the method used to calculate control limits, the range chart selected for the standard, and the way the data is coded for Short Run charts. |
102 and 106 |
|
Lower control
limit for the X or X-bar chart. This value is affected by
the method used to calculate control limits, the range chart selected
for the standard, and the way the data is coded for Short Run
charts. |
100 and 104 |
|
LCLx for zones |
Lower subgroup control limit used for zone checking when the Lower Control limit cannot be less than zero check box is selected in the standard. |
108 and 109 |
Moving average LCLr |
Lower control limit for the moving average range chart. This value is affected by the method used to calculate control limits, the range chart selected for the standard, and the way the data is coded for Short Run charts. |
185 |
Moving average LCLx |
Lower control
limit for the moving average chart. This value is affected
by the method used to calculate control limits, the range chart
selected for the standard, and the way the data is coded for Short
Run charts. |
182 |
Moving average mean |
The average of the moving average values displayed on the chart. The moving averages are calculated from the retrieved data using the Moving average span. |
181 |
Moving average R-Bar |
The average of the moving average range values displayed on the chart. The moving average range values are calculated from the retrieved data using the Moving average span. |
184 |
Moving average UCLr |
Upper control limit for the moving average range chart. This value is affected by the method used to calculate control limits, the range chart selected for the standard, and the way the data is coded for Short Run charts. |
183 |
Moving average UCLx |
Upper control
limit for the moving average chart. This value is affected
by the method used to calculate control limits, the range chart
selected for the standard, and the way the data is coded for Short
Run charts. |
180 |
Trend LCLx |
Lower control limit for a trend chart that is calculated from the spread of data around the linear regression line that best fits the data. |
151 and 155 |
Trend UCLx |
Upper control limit for a trend chart that is calculated from the spread of data around the linear regression line that best fits the data. |
150 and 154 |
Trend Y-intercept LCLx |
The value where the lower trend control limit intersects the Y axis. |
153 and 157 |
Trend Y-intercept UCLx |
The value where the upper trend control limit intersects the Y axis. |
152 and 156 |
Upper control limit for the range chart. This value is affected by the method used to calculate control limits, the range chart selected for the standard, and the way the data is coded for Short Run charts. |
103 and 107 |
|
Upper control
limit for the X or X-bar chart. This value is affected by
the method used to calculate control limits, the range chart selected
for the standard, and the way the data is coded for Short Run
charts. |
101 and 105 |
Default label |
Explanation |
Code(s) |
Maximum range |
Maximum value in the calculated set of range values. This includes range values for subgroups that are bypassed or statistical outliers. |
53 and 57 |
Maximum range included |
Maximum value in the calculated set of range values that are not excluded. |
62 and 76 |
Maximum range not bypassed |
Maximum value in the calculated set of range values that are not bypassed. |
239 and 243 |
Maximum subgroup |
Maximum subgroup value in the retrieved data. This includes subgroups that are bypassed or statistical outliers. |
51 |
Maximum subgroup included |
Maximum subgroup value in the retrieved data that is not excluded. |
59 |
Maximum subgroup not bypassed |
Maximum subgroup value in the retrieved data that is not bypassed. |
237 |
Maximum value |
Maximum individual value in the retrieved data. This includes values associated with subgroups that are bypassed or statistical outliers. |
55 |
Maximum value included |
Maximum individual value in the retrieved data that is not part of an excluded subgroup. |
65 |
Maximum value not bypassed |
Maximum individual value in the retrieved data that is not part of a bypassed subgroup. |
241 |
Minimum range |
Minimum value in the calculated set of range values. This includes range values for subgroups that are bypassed or statistical outliers. |
54 and 58 |
Minimum range included |
Minimum value in the calculated set of range values that is not excluded. |
63 and 77 |
Minimum range not bypassed |
Minimum value in the calculated set of range values that is not bypassed. |
240 and 244 |
Minimum subgroup |
Minimum subgroup value in the retrieved data. This includes subgroups that are bypassed or statistical outliers. |
52 |
Minimum subgroup included |
Minimum subgroup value in the retrieved data that is not excluded. |
60 |
Minimum subgroup not bypassed |
Minimum subgroup value in the retrieved data that is not bypassed. |
238 |
Minimum value |
Minimum individual value in the retrieved data. This includes values associated with subgroups that are bypassed or statistical outliers. |
56 |
Minimum value included |
Minimum subgroup value in the retrieved data that is not part of an excluded subgroup. |
66 |
Minimum value not bypassed |
Minimum subgroup value in the retrieved data that is not part of a bypassed subgroup. |
242 |
Default label |
Explanation |
Code |
Offset Percentage |
Percentage that
the mean is different from the target, based on specs. |
40 |
% above lower Spec |
Percent of included
values above the lower specification limit. |
255 |
% above Spec |
Percent of included
values above the upper specification limit. |
68 |
% above Spec predicted |
Percent of values
predicted to fall above the upper specification limit based on
the fitted curve. This value is not reliable with small sample
sizes. |
80 |
% below Spec |
Percent of included
values below the lower specification limit. |
69 |
% below Spec predicted |
Percent of values
predicted to fall below the lower specification limit based on
the fitted curve. This value is not reliable with small sample
sizes. |
79 |
% below upper Spec |
Percent of included
values below the upper specification limit. |
256 |
% in Spec |
Percent of included
values between the upper and lower specification limits. |
70 |
% in Spec predicted |
Percent of values
predicted to fall inside the upper and lower specification limits
based on the fitted curve. This value is not reliable with small
sample sizes. |
82 |
Percent of included
values outside the upper and lower specification limits. |
71 |
|
% out of Spec predicted |
Percent of values
predicted to fall outside the upper and lower specification limits
based on the fitted curve. This value is not reliable with small
sample sizes. |
81 |
Count above Spec |
Count of included
values above the upper specification limit. |
211 |
Count above Spec predicted |
Number of values
predicted to fall above the upper spec limit based on the fitted
curve. This value is not reliable with small sample sizes. |
287 |
Count below Spec |
Count of included
values below the lower specification limit. |
212 |
Count below Spec predicted |
Number of values
predicted to fall below the lower spec limit based on the fitted
curve. This value is not reliable with small sample sizes. |
288 |
Count in Spec |
Count of included
values between the upper and lower specification limits. |
195 |
Count in Spec predicted |
Number of data
values predicted to fall between the upper and lower spec limits
based on the fitted curve. This value is not reliable with small
sample sizes. |
289 |
Count out of Spec |
Count of included
values outside the upper and lower specification limits. |
194 |
Count out of Spec predicted |
Number of data
values predicted to fall outside the upper and lower spec limits
based on the fitted curve. This value is not reliable with small
sample sizes. |
290 |
Mean - 3SD within Spec |
If Mean
– 3SD falls above the lower spec, this returns "Yes". |
91 |
Mean - 4SD within Spec |
If Mean
– 4SD falls above the lower spec, this returns "Yes". |
93 |
Mean + 3SD within Spec |
If Mean
+ 3SD falls below the upper spec, this returns "Yes". |
90 |
Mean + 4SD within Spec |
If Mean
+ 4SD falls below the upper spec, this returns "Yes". |
92 |
PPM above Spec |
PPM of included
values above the upper specification limit. |
72 |
PPM above Spec predicted |
PPM of values predicted
to fall above the upper specification limit based on the fitted
curve. This value is not reliable with small sample sizes. |
84 |
PPM below Spec |
PPM of included
values below the lower specification limit. |
73 |
PPM below Spec predicted |
PPM of values predicted
to fall below the lower specification limit based on the fitted
curve. This value is not reliable with small sample sizes. |
83 |
PPM in Spec |
PPM of included
values between the upper and lower specification limits. |
74 |
PPM in Spec predicted |
PPM of values predicted
to fall inside the upper and lower specification limits based
on the fitted curve. This value is not reliable with small sample
sizes. |
86 |
PPM out of Spec |
PPM of included
values outside the upper and lower specification limits. |
75 |
PPM out of Spec predicted |
PPM of values predicted
to fall outside the upper and lower specification limits based
on the fitted curve. This value is not reliable with small sample
sizes. |
85 |
Default label |
Explanation |
Code |
First quartile |
The value below which 25% of the ranked data values lie. |
229 |
The value below
which one would expect to find .135 percent of the values from
a data set. |
88 |
|
Mean - 3SD within Spec |
If Mean
– 3SD falls above the lower spec, this returns "Yes". |
91 |
The value below
which one would expect to find .003 percent of the values from
a data set. |
95 |
|
Mean -4SD within Spec |
If Mean
– 4SD falls above the lower spec, this returns "Yes". |
93 |
The value above
which one would expect to find .135 percent of the values from
a data set. |
87 |
|
Mean + 3SD within Spec |
If Mean
+ 3SD falls below the upper spec, this returns "Yes". |
90 |
The value above
which one would expect to find .003 percent of the values from
a data set. |
94 |
|
Mean + 4SD within Spec |
If Mean
+ 4SD falls below the upper spec, this returns "Yes". |
92 |
The spread within which one would expect to find 99.9973 percent of the data values. This value is calculated based on the Method for calculating standard deviation setting and type of data distribution (Normal or Non-normal). |
89 |
|
Third quartile |
The value above which 25% of the ranked data values lie. |
230 |
Default label |
Explanation |
Code |
% above Control |
Percent of subgroups that are not bypassed that fall above the upper control limit (UCLx). |
163 |
Percent of subgroups
that are not bypassed that fall above the upper Gate limit. |
167 |
|
Percent of included
values that fall above the upper Ind. Gate limit. |
249 |
|
% above lower Gate |
Percent of subgroups
that are not bypassed that fall above the lower Gate limit. |
257 |
% above lower Ind. Gate |
Percent of included
values that fall above the lower Ind. Gate limit. |
253 |
% above lower Spec |
Percent of included
values above the Lower Spec. |
255 |
% above Range Gate |
Percent of included values above
the Range Gate. |
314 |
% above Spec |
Percent of included
values above the Upper Spec. |
68 |
% above Spec predicted |
Percent of values
predicted to fall above the Upper Spec based on the fitted curve.
This value is not reliable with small sample sizes. |
80 |
Percent of subgroups
that are not bypassed that fall above the Target
X. |
214 |
|
% below Control |
Percent of subgroups that are not bypassed that fall below the lower control limit (LCLx). |
164 |
Percent of subgroups
that are not bypassed that fall below the lower Gate limit. |
168 |
|
Percent of included
values that fall below the lower Ind. Gate limit. |
250 |
|
% below Spec |
Percent of included
values below the Lower Spec. |
69 |
% below Spec predicted |
Percent of values
predicted to fall below the Lower Spec based on the fitted curve.
This value is not reliable with small sample sizes. |
79 |
% below target |
Percent of subgroups
that are not bypassed that fall below the Target
X. |
216 |
% below upper Gate |
Percent of subgroups
that are not bypassed that fall below the upper Gate limit. |
258 |
% below upper Ind. Gate |
Percent of included
values that fall below the upper Ind. Gate limit. |
254 |
% below upper Spec |
Percent of included
values below the Upper Spec. |
256 |
% in Control |
Percent of subgroups that are not bypassed that fall between the upper control limit (UCLx) and the lower control limit (LCLx). |
166 |
% in Gate |
Percent of subgroups
that are not bypassed that fall between the upper and lower Gate
limits. |
170 |
% in Ind. Gate |
Percent of subgroups
that are not bypassed that fall between the upper and lower Ind.
Gate limits. |
252 |
% in Spec |
Percent of included
values between the upper and lower specification limits. |
70 |
% in Spec predicted |
Percent of values
predicted to fall inside the upper and lower specification limits
based on the fitted curve. This value is not reliable with small
sample sizes. |
82 |
% out of Control |
Percent of subgroups that are not bypassed that fall above the upper control limit (UCLx) or below the lower control limit (LCLx). |
165 |
% out of Gate |
Percent of subgroups
that are not bypassed that fall outside the upper and lower Gate
limits. |
169 |
% out of Ind. Gate |
Percent of subgroups
that are not bypassed that fall outside the upper and lower Ind.
Gate limits. |
251 |
% out of Spec |
Percent of included
values outside the upper and lower specification limits. |
71 |
% out of Spec predicted |
Percent of values
predicted to fall outside the upper and lower specification limits
based on the fitted curve. This value is not reliable with small
sample sizes. |
81 |
% subgroups within 1 sigma |
Percent of subgroups
that are not bypassed that fall within 1 sigma from the mean. |
188 |
% subgroups within 2 sigma |
Percent of subgroups
that are not bypassed that fall within 2 sigma from the mean. |
189 |
Default label |
Explanation |
Code |
Bypassed subgroups |
Number of subgroups set to Bypass record or Include on charts and data lists only. |
234 |
Bypassed values |
Number of data values associated with subgroups set to Bypass record or Include on charts and data lists only. |
233 |
Count above Control |
Number of subgroups that are not bypassed that fall above the upper control limit (UCLx). |
245 |
Count above Gate predicted |
Number of subgroups
predicted to fall above the upper gate limit based on the fitted
curve. This value is not reliable with small sample sizes. |
295 |
Count above Ind. Gate predicted |
Number of values
predicted to fall above the upper Ind. Gate limit based on the
fitted curve. This value is not reliable with small sample sizes. |
291 |
Count above Range Gate |
Number of values above the range
gate. |
315 |
Count above Spec |
Count of included
values above the upper specification limit. |
211 |
Count above Spec predicted |
Number of values
predicted to fall above the upper spec limit based on the fitted
curve. This value is not reliable with small sample sizes. |
287 |
Count above target |
Number of subgroups
that are not bypassed that fall above the Target
X. |
213 |
Count Anchor point |
Number of subgroups in the retrieved data that are marked as Anchor points. |
210 |
Count below Control |
Number of subgroups that are not bypassed that fall below the lower control limit (LCLx). |
246 |
Count below Gate predicted |
Number of subgroups
predicted to fall below the lower gate limit based on the fitted
curve. This value is not reliable with small sample sizes. |
296 |
Count below Ind. Gate predicted |
Number of values
predicted to fall below the lower Ind. Gate limit based on the
fitted curve. This value is not reliable with small sample sizes. |
292 |
Count below Spec |
Count of included
values below the lower specification limit. |
212 |
Count below Spec predicted |
Number of values
predicted to fall below the lower spec limit based on the fitted
curve. This value is not reliable with small sample sizes. |
288 |
Count below target |
Number of subgroups
that are not bypassed that fall below the Target
X. |
215 |
Count data groups |
Number of data groups based on the Data grouped by setting. |
231 |
Count excluded subgroups |
Number of subgroups that are excluded as outliers or bypassed records. |
8 |
Count excluded values |
Number of individual values associated with subgroups that are excluded as outliers or bypassed records. |
5 |
Count in Control |
Number of subgroups that are not bypassed that fall between the upper control limit (UCLx) and the lower control limit (LCLx). |
248 |
Count in Gate predicted |
Number of subgroups
predicted to fall between the upper and lower gate limits based
on the fitted curve. This value is not reliable with small sample
sizes. |
297 |
Count in Ind. Gate predicted |
Number of subgroups
predicted to fall between the upper and lower Ind. Gate limits
based on the fitted curve. This value is not reliable with small
sample sizes. |
293 |
Count in Spec |
Count of included
values between the upper and lower specification limits. |
195 |
Count in Spec predicted |
Number of data
values predicted to fall between the upper and lower spec limits
based on the fitted curve. This value is not reliable with small
sample sizes. |
289 |
Count included subgroups |
Number of subgroups that are not excluded as outliers or bypassed records. |
7 |
Count included values |
Number of individual values associated with subgroups that are not excluded as outliers or bypassed records. |
4 |
Count incomplete subgroup values |
Number of subgroups that contain one or more data values marked as missing. |
284 |
Count out of Control |
Number of subgroups that are not bypassed that fall above the upper control limit (UCLx) or below the lower control limit (LCLx). |
247 |
Count out of Gate predicted |
Number of subgroups
predicted to fall outside the upper and lower gate limits based
on the fitted curve. This value is not reliable with small sample
sizes. |
298 |
Count out of Ind. Gate predicted |
Number of subgroups
predicted to fall outside the upper and lower Ind. Gate limits
based on the fitted curve. This value is not reliable with small
sample sizes. |
294 |
Count out of Spec |
Count of included
values outside the upper and lower specification limits. |
194 |
Count out of Spec predicted |
Number of data
values predicted to fall outside the upper and lower spec limits
based on the fitted curve. This value is not reliable with small
sample sizes. |
290 |
Count subgroups not bypassed |
Number of subgroups that are set to Include record. |
235 |
Count subgroups with all missing values |
Number of subgroups where all of the data values are marked as missing. |
283 |
Count subgroups within 1 sigma |
Number of subgroups
that are not bypassed that fall within 1 sigma from the mean. |
299 |
Count subgroups within 3 sigma |
Number of subgroups
that are not bypassed that fall within 2 sigma from the mean. |
300 |
Count values not bypassed |
Number of data values associated with subgroups set to Include record. |
236 |
Total subgroups |
Number of subgroups in the retrieved data. This number includes excluded subgroups. |
6 |
Total values |
Number of individual values in the retrieved data. This number includes individual values associated with excluded subgroups. |
3 |
Default label |
Explanation |
Code |
A1 |
Root (where the
fitted curve crosses the X-axis) to the left of the mean. |
110 |
A2 |
Root (where the
fitted curve crosses the X-axis) to the right of the mean. |
111 |
Chi-squared |
The chi-square
statistic is calculated
by finding the difference between each observed and theoretical
frequency for each possible outcome. |
139 |
Chi-squared hypothesis |
“Accepted” or “Rejected”
based on the Chi-squared value and degrees
of freedom in the data set. |
138 |
The curve type
that best fits the data retrieved. May be one of the following: |
117 |
|
Insufficient non-normal resolution |
Returns "Yes" if the non-normal analysis lacks sufficient resolution to make valid statistical calculations. |
302 |
Kurtosis |
Kurtosis describes the peakedness of the data. |
120 |
Kurtosis test |
Returns “Pass”
if the Kurtosis value falls within high and low values defined
for the number of data values in the data set. |
116 |
M1 |
Power (steepness
of the fitted curve) to the left of the mean. |
112 |
M2 |
Power (steepness
of the fitted curve) to the right of the mean. |
113 |
Non-normal area |
Area underneath
the non-normal curve. |
114 |
Skewness |
Skewness describes how non-symmetrical the data are on either side of a vertical axis through the mean. |
119 |
Skewness test |
Returns “Pass”
if the Skewness value falls below the critical value defined for
the number of data values in the data set. |
115 |
Spread used |
For a Normal Distribution, this returns “Calculated”. |
118 |
Default label |
Explanation |
Code(s) |
Trend correlation coefficient |
A measure of the
interdependence of x and y values on a trend chart. |
140 and 146 |
Returns the x value where the current trend line is expected to cross the closest specification limit displayed on the trend chart. |
144 and 145 |
|
Returns the number of future subgroups at which the current trend line is expected to cross the closest specification limit displayed on the trend chart. Calculated as Trend crosses at - Total subgroups You can create a custom statistic that multiplies this statistic by a cycle time to return the predicted time to failure. |
319 |
|
Trend LCLx |
Lower control limit for a trend chart that is calculated from the spread of data around the linear regression line that best fits the data. |
151 and 155 |
Trend line |
The line that best
fits the data on the trend chart |
141 and 147 |
Trend slope |
The slope of the line that best fits the data on a trend chart. |
142 and 148 |
Trend UCLx |
Upper control limit for a trend chart that is calculated from the spread of data around the linear regression line that best fits the data. |
150 and 154 |
Trend Y-intercept |
The y value when x = 0 for the line that best fits the data on a trend chart. |
143 and 149 |
Trend Y-intercept LCLx |
The value where the lower trend control limit intersects the Y axis. |
153 and 157 |
Trend Y-intercept UCLx |
The value where the upper trend control limit intersects the Y axis. |
152 and 156 |
Default label |
Explanation |
Code |
Current date |
Returns the current date. |
219 |
Current date/time |
Returns the current date and time. |
218 |
Current time |
Returns the current time. |
220 |
High date queried |
Returns the high
date used to query the data. |
221 |
High date retrieved |
Returns the date from the latest date/time in the retrieved data set. |
223 |
High date/time queried |
Returns the high
date and time used to query the data. |
11 |
High date/time retrieved |
Returns the latest date/time in the retrieved data set. |
161 |
High time queried |
Returns the high
time used to query the data. |
222 |
High time retrieved |
Returns the time from the latest date/time in the retrieved data set. |
224 |
Low date queried |
Returns the low
date used to query the data. |
225 |
Low date retrieved |
Returns the date from the earliest date/time in the retrieved data set. |
227 |
Low date/time queried |
Returns the low
date and time used to query the data. |
12 |
Low date/time retrieved |
Returns the earliest date/time in the retrieved data set. |
162 |
Low time queried |
Returns the low
time used to query the data. |
226 |
Low time retrieved |
Returns the time from the earliest date/time in the retrieved data set. |
228 |
Default label |
Explanation |
Code |
Add groups for varying subgroup sizes |
One of the Varying
subgroup size settings. |
268 |
Amount of time to display |
Returns the time precision for reported date/time values based on the current Show time to setting. |
274 |
CuSum acceptance limit type |
Returns the current Acceptance limit based on setting. |
301 |
Returns the current Decision interval value setting. |
203 |
|
CuSum start value constant |
Returns the current Start value constant setting. |
202 |
Evaluate more data sets as non-normal |
Returns “Yes” or “No” based on the current Evaluate more data sets as non-normal setting. |
276 |
EWMA weight |
Returns the current EWMA weight setting. |
278 |
Exclude varying subgroup size (all) |
One of the Varying
subgroup size settings. |
303 |
Exclude varying subgroup size (degrees of freedom) |
One of the Varying subgroup size settings. |
272 |
Exclude varying subgroup size (percent) |
One of the Varying subgroup size settings. |
271 |
Force distribution |
Returns the current Force distribution setting. |
275 |
Limit non-normal slices |
Returns “Yes” or “No” based on the current Limit number of slices for non-normal area calculation setting. |
197 |
Moving average span |
Returns the current Moving average span setting. |
186 |
Non-symmetrical Control limits |
Returns “Yes” or “No” based on the current Calculate non-symmetrical control limits for subgroup size = 1 setting. |
267 |
Run length |
Returns the current Run length setting. |
9 |
Runs based on |
Returns the current Run value based on setting. |
270 |
Standardize data for varying subgroup size |
One of the Varying
subgroup size settings. |
273 |
Trend chart limits |
Returns the current Trend chart limits selections. |
277 |
Default label |
Explanation |
Code |
Returns the Data entry constant setting from the current SPC standard or Short Run process specification. |
158 |
|
Returns the Decimal places setting from the current SPC standard or Short Run process specification. |
1 |
|
Returns the Description setting from the current SPC standard or Short Run process specification. |
16 |
|
The DMS Part Number set on the DMS Data Entry tab of the current SPC standard or Short Run process specification. |
265 |
|
The DMS Process set on the DMS Data Entry tab of the current SPC standard or Short Run process specification. |
266 |
|
Returns the Exponent setting from the current SPC standard or Short Run process specification. |
193 |
|
Returns "Yes" or "No" based on the Lower Control limit cannot be less than zero setting from the current SPC standard or Short Run process specification. |
200 |
|
Returns “English”, “Metric”, or “Not set” based on the Measurement system setting from the current SPC standard or Short Run process specification. |
17 |
|
Returns the Measurement unit setting from the current SPC standard or Short Run process specification. |
18 |
|
Returns the name of the SPC standard or Short Run process specification that is associated with this data retrieval. |
10 |
|
Returns “Range”, “Moving Range”, “Sigma” or “Not set” based on the Range chart setting from the current SPC standard or Short Run process specification. |
19 |
|
Returns the current list of real-time checks based on the Real-time checks setting from the current SPC standard or Short Run process specification. |
279 |
|
Returns the Upper Value setting for Range Scaling from the current SPC standard or Short Run process specification. |
190 |
|
Returns the Upper Value setting for X-bar and Performance Chart Scaling from the current SPC standard or Short Run process specification. |
191 |
|
Returns the Lower Value setting for X-bar and Performance Chart Scaling from the current SPC standard or Short Run process specification. |
192 |
|
Short Run index |
Returns the number
of the traceability
field (1-6) on which a short run retrieval is based. |
281 |
Short Run method |
Returns the Short Run method setting from
the current Short Run process specification. |
15 |
Returns the value
of the Standard flags
database field from the current SPC standard or Short Run process specification: |
280 |
|
Returns the subgroup
size for the current SPC standard. |
261 |
|
Returns the Standard variable 1 setting from the current SPC standard or Short Run process specification. |
96 |
|
Standard variable 2 |
Returns the Standard variable 2 setting from the current SPC standard or Short Run process specification. |
97 |
Standard variable 3 |
Returns the Standard variable 3 setting from the current SPC standard or Short Run process specification. |
98 |
Standard variable 4 |
Returns the Standard variable 4 setting from the current SPC standard or Short Run process specification. |
99 |
Returns the Target R setting from the current SPC standard or Short Run process specification. |
263 |
|
Returns the Target X setting from the current SPC standard or Short Run process specification. |
262 |
|
Returns “Yes” or “No” based on the Use exponential notation setting from the current SPC standard or Short Run process specification. |
282 |
Default label |
Explanation |
Code |
Returns the Lower Gate setting from the current SPC standard or Short Run process specification. |
30 |
|
Returns the Lower Ind. Gate setting from the current SPC standard or Short Run process specification. |
34 |
|
Returns the Lower range Gate setting from the current SPC standard or Short Run process specification. |
46 |
|
Returns the Lower Reasonable limit setting
from the current SPC standard or Short Run process specification. |
38 |
|
Returns the Lower Spec setting from the current SPC standard or Short Run process specification. |
42 |
|
Nominal Gate |
If Lower Gate and
Upper Gate are set in the current SPC standard or Short Run process
specification, then Nominal Gate equals the midpoint between Lower
Gate and Upper Gate. |
32 |
Nominal Ind. Gate |
If Lower Ind. Gate
and Upper Ind. Gate are set in the current SPC standard or Short
Run process specification, then Nominal Ind. Gate equals the midpoint
between Lower Ind. Gate and Upper Ind. Gate. |
36 |
If Lower range
Gate and Upper range Gate are set in the current SPC standard
or Short Run process specification, then Nominal range Gate equals
the midpoint between Lower range Gate and Upper range Gate. |
48 |
|
If Target
X is set in the current SPC standard or Short Run process
specification, then Nominal Spec equals Target X. |
44 |
|
Tolerance Gate |
If Lower Gate and
Upper Gate are set in the current SPC standard or Short Run process
specification, then Tolerance Gate equals the difference between
Lower Gate and Upper Gate. |
33 |
Tolerance Ind. Gate |
If Lower Ind. Gate
and Upper Ind. Gate are set in the current SPC standard or Short
Run process specification, then Tolerance Ind. Gate equals the
difference between Lower Ind. Gate and Upper Ind. Gate. |
37 |
If Lower range
Gate and Upper range Gate are set in the current SPC standard
or Short Run process specification, then Tolerance range Gate
equals the difference between Lower range Gate and Upper range
Gate. |
49 |
|
If Lower Spec and
Upper Spec are set in the current SPC standard or Short Run process
specification, then Tolerance Spec equals the difference between
Lower Spec and Upper Spec. |
45 |
|
Returns the Upper Gate setting from the current SPC standard or Short Run process specification. |
31 |
|
Returns the Upper Ind. Gate setting from the current SPC standard or Short Run process specification. |
35 |
|
Returns the Upper range Gate setting from the current SPC standard or Short Run process specification. |
47 |
|
Returns the Upper Reasonable limit setting
from the current SPC standard or Short Run process specification. |
39 |
|
Returns the Upper Spec setting from the current SPC standard or Short Run process specification. |
43 |
Default label |
Explanation |
Code |
Column |
Specifies the column used if only one column of data was retrieved. |
41 |
Conversion multiplier |
Returns the current Conversion multiplier setting. |
305 |
Date period |
Returns the current Date period setting. |
208 |
Returns the current Statistical outliers setting. |
22 |
|
Filter contents |
Returns the filter
contents associated with Filter
name. |
14 |
Filter name |
Returns the current
Filter
name setting. |
13 |
High date/time queried |
Returns the high
date and time used to query the data (based on the current Filter
name setting). |
11 |
Low date/time queried |
Returns the low
date and time used to query the data (based on the current
Filter
name setting). |
12 |
Maximum count for retrieval |
Returns the current Maximum count for retrieval setting. |
2 |
Method used to calculate Control limits |
Returns the current Method used to calculate Control limits setting. |
21 |
Non-normal method |
Returns “Yes” or “No” based on the current Use the median method to calculate Z values instead of probability method setting. |
50 |
Paired Sample Grouping |
Returns the current Traceability grouped by setting for Paired Sample analysis. |
318 |
SQL query statement |
Returns the SQL query statement used to retrieve the data. |
209 |
Standard deviation method |
Returns the current Method for calculating standard deviation setting. |
20 |
Default label |
Explanation |
Code |
| Brushed data | Returns "Yes" to indicate that the current data is partial data from the original retrieval. Otherwise, it returns "No". | 269 |
CuSum acceptance limit |
CuSum acceptance
limit is calculated as Upper
Limit – Target. |
201 |
CuSum high sample unit tolerance |
Returns the CuSum C2
value. |
207 |
CuSum low sample unit tolerance |
Returns the CuSum C1
value. |
206 |
CuSum start value |
Returns the CuSum S
value. |
205 |
Returns the type
of grouping used to calculate control limits for the data set. |
232 |
|
Reflects whether the entire retrieved data set exhibits a state of statistical control, including subgroups that are excluded as outliers. If any retrieved data is outside control limits or exhibits control chart signals for runs, trends, or zones, this statistic returns “No”; otherwise, it returns “Yes”. |
217 |
|
Returns the number
of degrees of freedom found in the data set. |
260 |
|
Drill-down conditions |
Returns a list of drill-down actions taken up to the current data set. If no drill-down action is taken, it returns "None". |
306 |
External data |
Returns "Yes" if data originates from an external source. Otherwise, it returns "No." |
307 |
Kruskal-Wallis 0.01 limit |
Chi-squared value
for significance of 0.01. |
174 |
Kruskal-Wallis 0.10 limit |
Chi-squared value
for significance of 0.10. |
173 |
Kruskal-Wallis test |
Returns “Pass”,
“Fail” or “Uncertain”. |
171 |
Kruskal-Wallis value |
Returns Kruskal-Wallis
test statistic |
172 |
Last Action Taken |
Returns the most recent action taken, which may be blank. |
311 |
Last Cause |
Returns the most recent cause, which may be blank. |
310 |
Last Event |
Returns the most recent event, which may be blank. |
309 |
Last Note |
Returns the note for the most recent retrieval, which may be blank. |
312 |
Last Part Number |
Returns the name of the last standard for the most recent record. |
313 |
Last X-Bar |
Returns the X-Bar value for the most recent record. | 308 |
Returns the name of the Dashboard Retrieval if used or "NA" if no Dashboard Retrieval was used. |
317 |
|
Sum values squared |
Returns the sum of the squares of all included values in the data set. |
199 |
Variance |
Returns SD
(sample) squared. |
159 |
Varying subgroup sizes found |
Returns “Yes” or “No” based on whether the data contains incomplete subgroups or varying subgroup sizes. |
259 |
Returns the Windows login name for the Windows user currently logged in on the workstation. |
316 |
|
X-bar chart all inside Control |
Returns “Yes” or “No” based on whether all subgroups on the X-bar chart fall inside the control limits. |
175 |